En standard, Windows Server 2008 R2 contient PowerShell 2.0 et Windows Server 2012 contient PowerShell 3.0. Il est possible d’installer PowerShell 4.
Table des matières
Pour un Windows Server 2008 R2 (ou un Windows 7)
- Installer Microsoft .NET Framework 4.5, 4.5.1 ou 4.5.2 (nécessite un reboot)
- (Facultatif) Installer le module linguistique pour 4.5 ou 4.5.1 ou 4.5.2
- Installer Windows Management Framework 4.0 (nécessite un reboot)
Attention à bien installer le .NET Framework 4.5.x avant WMF 4.0, sinon ce dernier s’installera, mais sans PowerShell.
Pour un Windows Server 2012 (ou un Windows 8)
- (Facultatif) Installer Microsoft .NET Framework 4.5.1 ou 4.5.2 (nécessite un reboot)
- (Facultatif) Installer le module linguistique pour 4.5.1 ou 4.5.2
- Installer Windows Management Framework 4.0 (nécessite un reboot)
Windows Management Framework 4.0
L’installation de Windows Management Framework 4.0 inclut Windows PowerShell 4.0, Windows PowerShell Web Services (Extension IIS Management OData), la Gestion à distance de Windows (WinRM), l’Infrastructure de gestion Windows (WMI) et une nouvelle fonction pour la version 4.0 : la configuration d’état souhaité (DSC) de Windows PowerShell.
Vérification
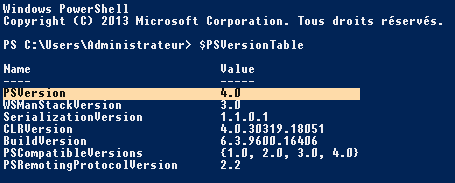
Pour vérifier la version de PowerShell installée : $PSVersionTable
Remarque
Je vous conseille d’installer le framework 4.5.2 car, à partir de janvier 2016, seule cette version sera supportée par Microsoft : Changement dans le support d’Internet Explorer et des Frameworks .NET